- 参考资料
- 1. What is git
- 2. Git Basics
- 3. Git Branching
- 5. Distributed Git
- 6. GitHub
- 7 Git Tools
参考资料
- Atassian git tutorials
- Pro Git
- Git 在 ZSH 下的快捷操作 zsh git cheatsheet
- Git tips
- 常用Git 清单
1. What is git
- To be efficient, if files have not changed, Git doesn’t store the file again, just a link to the previous identical file it has already stored. Git thinks about its data more like a stream of snapshots.
- states
- Modified means that you have changed the file but have not committed it to your database yet
- Staged means that you have marked a modified file in its current version to go into your next commit snapshot
- Committed means that the data is safely stored in your local database
- modified 就是你现在已经外出了,可能已经被病毒感染了,staged 就是已经进了医院观察治疗,committed 就是通过试剂确认无毒无害。
1.1 Global config
- /etc/gitconfig
- ~/.gitconfig or ~/.config/git/config
- .git/config
- Each level overrides values in the previous level, so values in .git/config trump those in /etc/gitconfig
1.2 Your Identity
$ git config --global user.name "John Doe"
$ git config --global user.email johndoe@example.com
1.3 Help
$ git help <verb>
$ git <verb> --help
$ man git-<verb>
$ git add -h
- you can ask for the more concise “help” output with the -h option, as in
2. Git Basics
基本操作
2.2 Recording Changes to the Repository
- You typically obtain a Git repository in one of two ways:
- You can take a local directory that is currently not under version control, and turn it into a Git repository, or
- You can clone an existing Git repository from elsewhere.
$ git clone https://github.com/libgit2/libgit2
# If you want to clone the repository into a directory named something other than libgit2
$ git clone https://github.com/libgit2/libgit2 mylibgit
- $ git status -s (more simplified)
- .gitignore 包含不需要track的文件,可以用正则
Here is another example .gitignore file:
# ignore all .a files
*.a
# but do track lib.a, even though you're ignoring .a files above
!lib.a
# only ignore the TODO file in the current directory, not subdir/TODO
/TODO
# ignore all files in any directory named build
build/
# ignore doc/notes.txt, but not doc/server/arch.txt
doc/*.txt
# ignore all .pdf files in the doc/ directory and any of its subdirectories
doc/**/*.pdf
# [https://github.com/github/gitignore](https://github.com/github/gitignore)
- –staged and –cached are synonyms
- git commit -am (-a 自动stag文件)
- git rm 删除文件
- 文件移动git不追踪
- git mv is one command instead of three
- $ mv README.md README
- $ git rm README.md
- $ git add README
2.3 Viewing the Commit History
对于团队来说 log history 就是发现谁引入了问题
- git log(之前忘记commit的是什么版本的时候,可以使用)
- git log -p -2(最近两次commit有啥不同)
- git log –stat(简单版本)
- git log –pretty=format:”%h - %an, %ar : %s” (alias gh=’git log’,方便以后看)
- git log –since=2.weeks (可以通过时间筛选–since, –after, –until, –before, –grep)
- git log -S function_name (根据名称来匹配)
# 大型项目,谁的代码引入了问题,直接通过 log 查看非常方便
$ git log --pretty="%h - %s" --author='Junio C Hamano' --since="2008-10-01" \
--before="2008-11-01" --no-merges -- t/
5610e3b - Fix testcase failure when extended attributes are in use
acd3b9e - Enhance hold_lock_file_for_{update,append}() API
f563754 - demonstrate breakage of detached checkout with symbolic link HEAD
d1a43f2 - reset --hard/read-tree --reset -u: remove unmerged new paths
51a94af - Fix "checkout --track -b newbranch" on detached HEAD
b0ad11e - pull: allow "git pull origin $something:$current_branch" into an unborn branch
2.4 Undoing Things
如果是自己忘记了某些文件,可以再加一个commit,如果团队的话每一个commit 都要有意义,最好不要加上版本号,让整个版本看起来更麻烦
合并commit
# 第二次的 commit 会代替第一次,第一次不会出现在repository history中
$ git commit -m 'initial commit'
$ git add forgotten_file
$ git commit --amend
让文件变成unstaged 状态
$ git reset HEAD CONTRIBUTING.md
2.5 Working with Remotes
本地多个远程仓库,如何操作?没明白,岂不是容易混乱
Show your remote
$ git remote (gr)
$ git remote -v (gr -v)
Adding remote repositories
$ git remote add pb https://github.com/paulboone/ticgit
$ git remote -v
Fetching and Pulling from Your Remotes
# git fetch command only downloads the data to your local repository — it doesn’t automatically merge it with any of your work or modify what you’re currently working on. 必须明确使用checkout 才能使用fetch 的内容
$ git fetch <remote>
# git pull command to automatically fetch and then merge that remote branch into your current branch.
$ git pull
Pushing to remotes
# This command works only if you cloned from a server to which you have write access and if nobody has pushed in the meantime.
$ git push origin master
Inspecting a Remote
$ git remote show origin (gr show origin)
Renaming and Removing Remotes
$ git remote rename pb paul
$ git remote
origin
paul
$ git remote remove paul
$ git remote
origin
2.6 Tagging
- Like most VCSs, Git has the ability to tag specific points in a repository’s history as being important. Typically, people use this functionality to mark release points (v1.0, v2.0 and so on).
Creating tags
- A lightweight tag is very much like a branch that doesn’t change — it’s just a pointer to a specific commit
- Annotated tags, however, are stored as full objects in the Git database.
Annotated Tags
$ git tag -a v1.4 -m "my version 1.4"
$ git show v1.4
#把之前的历史记录标记
$ git tag -a v1.2 9fceb02
Lightweight Tags
$ git tag v1.4-lw
$ git tag
Sharing Tags
$ git push origin v1.5
$ git push origin --tags
Deleting Tags
# 本地删除
$ git tag -d v1.4-lw
# server 删除
$ git push origin --delete <tagname>
Checking out Tags
# (2.0.0 就是一个tag)
$ git checkout 2.0.0
3. Git Branching
3.1 Branches in a Nutterminal
git init 只是默认创建一个master branch,并没有什么特殊的,也可以命名成别的
Creating a New Branch
# 创建了新的branch,指针 HEAD 指向当前正在指向的分支
$ git branch testing
# 看当前指针指向
$ git log --oneline --decorate
52c9468 (HEAD -> master, testing) master v1.0
183208e test
Switching Branches
a branch in Git is actually a simple file that contains the 40 character SHA-1 checksum of the commit it points to. 如果同一份文件有改动, git 如何处理?
$ git checkout testing (gco testing, gcm 是直接到 master)
$ gst
On branch testing
nothing to commit, working tree clean
# 这个时候 testing branch 的文件比 master 多一个
$ vim test.rb
$ ga .
$ gc -m "testing branch, first commit"
# 看commit 记录
$ git log --oneline --decorate --graph --all
# Creating a new branch and switching to it at the same time
git checkout -b (gcb)
3.2 Basic Branching and Merging
真实工作场景
$ git checkout -b iss53
# This is shorthand for:
$ git branch iss53
$ git checkout iss53
Create a branch to add the hotfix.
$ git checkout -b hotfix
Switched to a new branch 'hotfix'
$ vim index.html
$ git commit -a -m 'fixed the broken email address'
[hotfix 1fb7853] fixed the broken email address
1 file changed, 2 insertions(+)
After it’s tested, merge the hotfix branch, and push to production.
$ git checkout master
$ git merge hotfix
Updating f42c576..3a0874c
Fast-forward
index.html | 2 ++
1 file changed, 2 insertions(+)
# 删除hotfix
$ git branch -d hotfix
Deleted branch hotfix (3a0874c).
Switch back to your original user story and continue working.
$ git checkout master
Switched to branch 'master'
$ git merge iss53
Merge made by the 'recursive' strategy.
index.html | 1 +
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+)
Basic Merge Conflicts
同一个文件的修改就很有可能碰到merge 不了,要仔细对比
# visual merge tool and walks you through the conflicts
$ git mergetool
3.3 Branch Management
# merged 和 no-merged 可以看branch 情况,先要到master ,如果已经merge 就可以删除没用的 branch, 如果没用merge , git branch -d 会失败
$ git branch --no-merged
$ git branch --merged
# 如果不想checkout
$ git branch --no-merged master
3.4 Branching Workflows
- Many Git developers have a workflow that embraces this approach, such as having only code that is entirely stable in their master branch — possibly only code that has been or will be released. They have another parallel branch named develop or next that they work from or use to test stability
- When you’re branching and merging, everything is being done only in your Git repository — there is no communication with the server
3.5 Remote Branches
# 显示remote 的branch
$ git ls-remote
# origin” is the default name for a remote when you run git clone.
# booyah/master 如果执行下面的命令,origin 就被替换了
$ git clone -o booyah
Fetch
强制fetch, 参考 W3doc
# To synchronize your work with a given remote, 所有的分支都会下载
$ git fetch origin
# 下载某一个分支
$ git fetch origin test
$ git checkout master
$ git branch new-branch-to-save-current-commits
$
$ git fetch --all
$ git reset --hard origin/master
Pushing
Git 可以强制 push,参考 stackoverflow
# git push <remote> <branch>
git push origin serverfix
$ git push origin <your_branch_name> -f
3.6 Rebasing
- In Git, there are two main ways to integrate changes from one branch into another: the merge and the rebase
- rebasing makes for a cleaner history, 让整个脉络更加清晰,但是也隐藏了历史。Merge 则不同,如实反应,但是可能路径比较乱
- ou should never rebase commits once they’ve been pushed to a public repository
$ git checkout experiment $ git rebase master First, rewinding head to replay your work on top of it... Applying: added staged command
5. Distributed Git
5.1 Distributed Workflows
Centralized Workflow
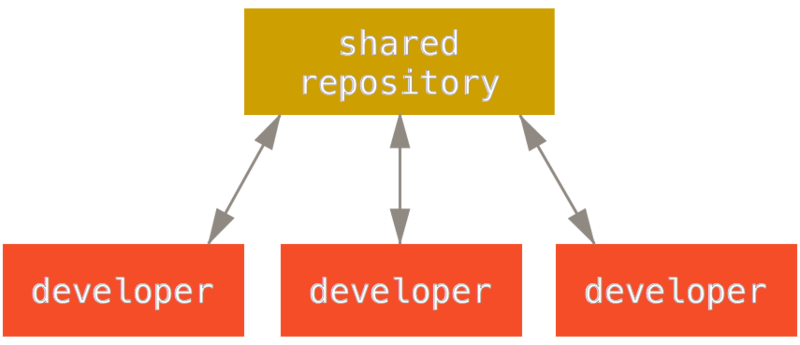
- This concept is as true in Git as it is in Subversion (or any CVCS), and this model works perfectly well in Git.
- With Git’s branching model, it’s possible for hundreds of developers to successfully work on a single project through dozens of branches simultaneously.
Integration-Manager Workflow
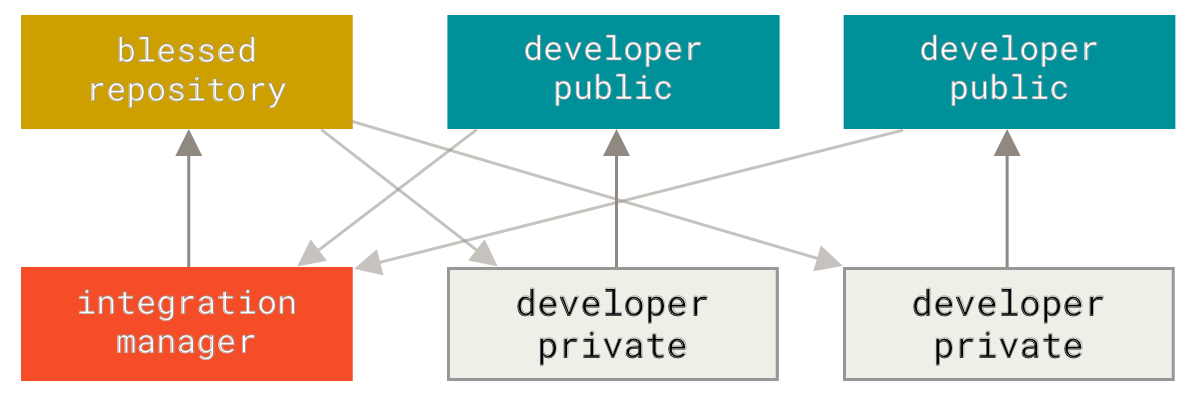
- One of the main advantages of this approach is that you can continue to work, and the maintainer of the main repository can pull in your changes at any time
- 这就是 GitHub 的方式, fork 一下开始自己的project, 每个人有自己独立的,也可以相互 pull
Dictator and Lieutenants Workflow
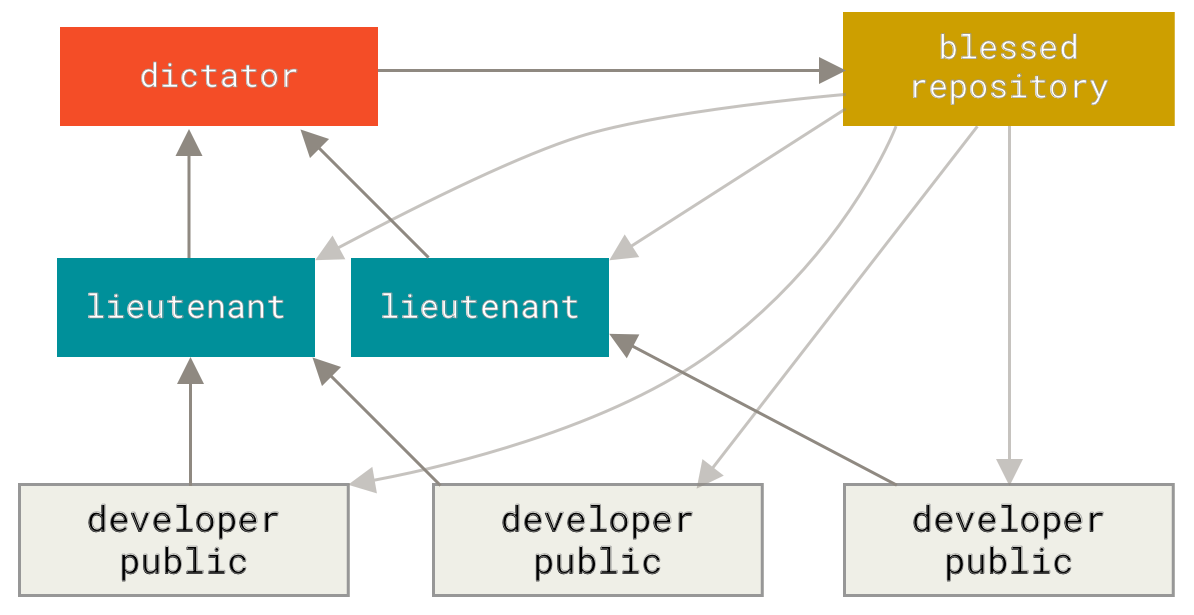
- One famous example is the Linux kernel
- This kind of workflow isn’t common, but can be useful in very big projects, or in highly hierarchical environments.
5.2 Contributing to a Project
- The main difficulty with describing how to contribute to a project are the numerous variations on how to do that.
- 几千人的大项目怎么做的?几百的人呢?
- 是否允许人commit ?
- 是否有一个integration manager?
- 那种模式管控的?
Commit Guidelines
# 检查是否有空格的错误
$ git diff --check
- Commit message. As a general rule, your messages should start with a single line that’s no more than about 50 characters and that describes the changeset concisely, followed by a blank line, followed by a more detailed explanation。平时都是gc -m 写博客可以,如果正式项目肯定不行
Capitalized, short (50 chars or less) summary
More detailed explanatory text, if necessary. Wrap it to about 72
characters or so. In some contexts, the first line is treated as the
subject of an email and the rest of the text as the body. The blank
line separating the summary from the body is critical (unless you omit
the body entirely); tools like rebase can get confused if you run the
two together.
Write your commit message in the imperative: "Fix bug" and not "Fixed bug"
or "Fixes bug." This convention matches up with commit messages generated
by commands like git merge and git revert.
Further paragraphs come after blank lines.
- Bullet points are okay, too
- Typically a hyphen or asterisk is used for the bullet, followed by a
single space, with blank lines in between, but conventions vary here
- Use a hanging indent
Private small team
- 如果只有几个人,使用方式和 cvs 类似,只不过要先fetch 、 merge 之后在push
$ git fetch origin
$ git merge origin/master
$ git push origin master
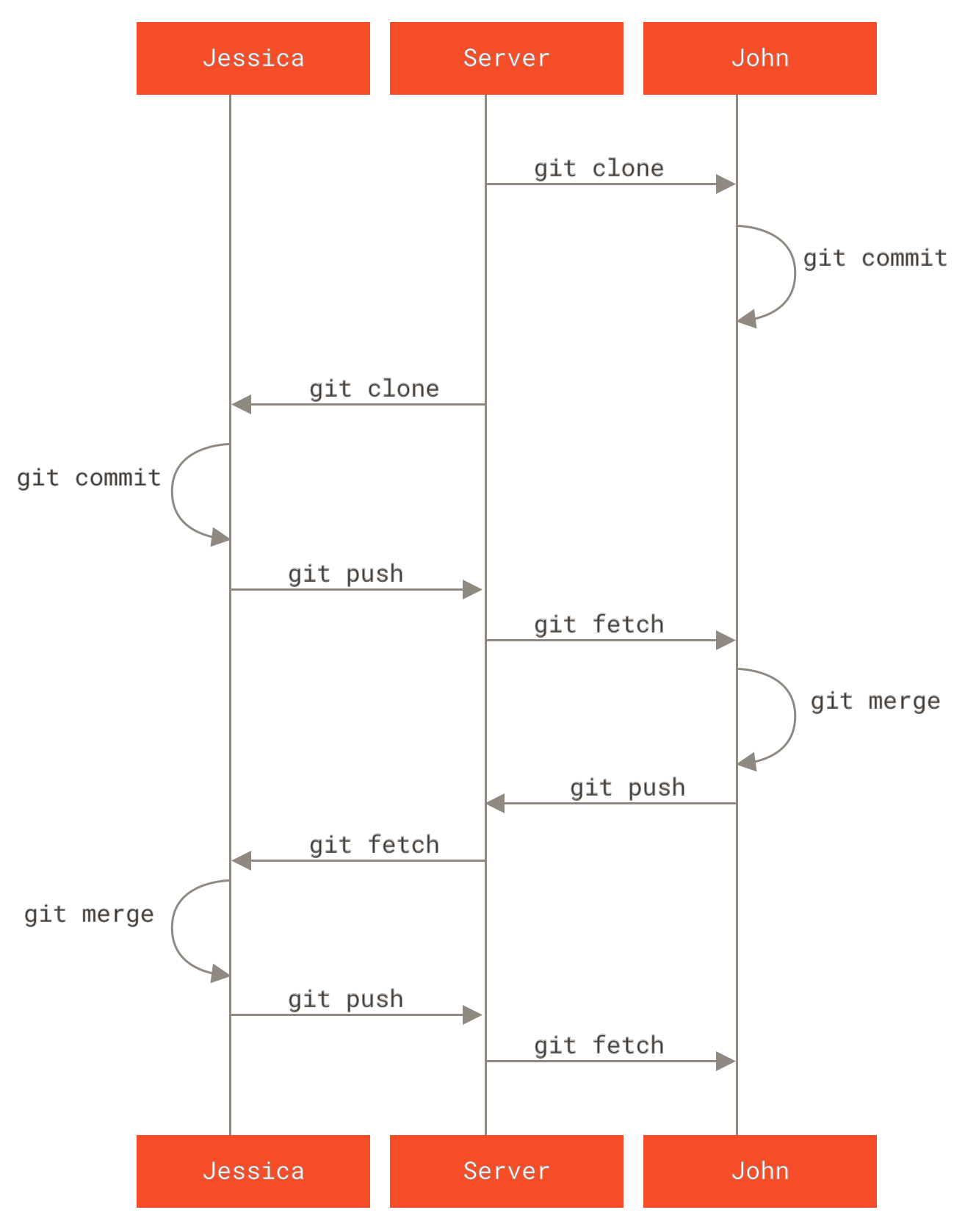
Private Managed Team
- master branch 由integration manager 来维护,team 各自维护一个 feature branch
- push -u 是啥意思?。是设置自己默认的 upstream,提前设置好一个默认映射关系在 repository 中,这样就可以直接git push origin, 而不是git push orgin master
# Jessica’s work on feature A
$ git checkout -b featureA
$ git push -u origin featureA
# Jessica decides to start working on featureB
$ git checkout -b featureB origin/master
$ vim lib/simplegit.rb
$ git commit -am 'made the ls-tree function recursive'
[featureB e5b0fdc] made the ls-tree function recursive
1 files changed, 1 insertions(+), 1 deletions(-)
$ vim lib/simplegit.rb
$ git commit -am 'add ls-files'
# Jessica 得知server featureB的 initial commit 已经push 上去,分支叫做 featureBee
$ git fetch origin
$ git merge origin/featureBee
# 以后自己的featureB 就push 到 server 的 featureBee
$ git push -u origin featureB:featureBee
Forked Public Project
fork 出来的直接加在remote 中即可,每个feature 要独立在一个branch,不然容易乱
- pull request: Once your work has been pushed to your fork of the repository, you need to notify the maintainers of the original project that you have work you’d like them to merge
$ git clone <url>
$ cd project
$ git checkout -b featureA
... work ...
$ git commit
... work ...
$ git commit
# When your branch work is finished and you’re ready to contribute it back to the maintainers, go to the original project page and click the “Fork” button,
$ git remote add myfork <url>
$ git push -u myfork featureA
# 通知原有项目人$ git checkout -b featureB origin/master
$ git request-pull origin/master myfork
The following changes since commit 1edee6b1d61823a2de3b09c160d7080b8d1b3a40:
Jessica Smith (1):
added a new function
are available in the git repository at:
git://githost/simplegit.git featureA
Jessica Smith (2):
add limit to log function
change log output to 30 from 25
lib/simplegit.rb | 10 +++++++++-
1 files changed, 9 insertions(+), 1 deletions(-)
# 如果要开始新的feature
# don’t continue working on the topic branch you just pushed up
$ git checkout -b featureB origin/master
# 如果 origin/master 和 feature 有冲突
# -f 是强制,也可以commit 到 server 的另一个featurev2
$ git checkout featureA
$ git rebase origin/master
$ git push -f myfork featureA
Public Project over Email
- Many projects have established procedures for accepting patches — you’ll need to check the specific rules for each project, because they will differ.
# format-patch 不太了解
$ git format-patch -M origin/master
# 可以通过git 直接发送邮件,在gitconfig中配置,下面的命令就可以直接发送邮件了
$ git send-email *.patch
5.2 Maintaining a Project
Working in Topic Branches
# 创建一个分支以便接受别人的request
$ git checkout -b sc/ruby_client master
Applying Patches from Email
需要重看,patch 和 pull request 有啥区别?
# 不懂, patch 和 pull request有什么不同?
$ git apply /tmp/patch-ruby-client.patch
# you can run git apply --check with the patch:
$ git apply --check 0001-seeing-if-this-helps-the-gem.patch
error: patch failed: ticgit.gemspec:1
error: ticgit.gemspec: patch does not apply
6. GitHub
6.2 Contributing to a Project
The GitHub Flow
- Fork the project
- Create a topic branch from master.
- Make some commits to improve the project.
- Push this branch to your GitHub project.
- Open a Pull Request on GitHub.
- Discuss, and optionally continue committing.
- The project owner merges or closes the Pull Request.
- Sync the updated master back to your fork.
7 Git Tools
7.1 Revision Selection
提供的回顾历史的方法
可以通过sha-1 跳转到制定的commit,即使sha-1 只有7位数字
$ git show 1c002dd4b536e7479fe34593e72e6c6c1819e53b
$ git show 1c002dd4b536e7479f
$ git show 1c002d
Branch References
# a log of where your HEAD and branch references have been for the last few months, reflog information is strictly local.it's like shell history
$ git reflog
734713b HEAD@{0}: commit: fixed refs handling, added gc auto, updated
d921970 HEAD@{1}: merge phedders/rdocs: Merge made by the 'recursive' strategy.
1c002dd HEAD@{2}: commit: added some blame and merge stuff
1c36188 HEAD@{3}: rebase -i (squash): updating HEAD
95df984 HEAD@{4}: commit: # This is a combination of two commits.
1c36188 HEAD@{5}: rebase -i (squash): updating HEAD
7e05da5 HEAD@{6}: rebase -i (pick): updating HEAD
$ git show HEAD@{5}
$ git show master@{yesterday}
# However, it can be helpful sometimes when you need to see what’s really going on. Here you can run rev-parse on your branch
$ git rev-parse topic1
HEAD^, which means “the parent of head
$ git show HEAD^
# 可以叠加
$ git show HEAD^^^
# 第三个 parent
$ git show d921970^3
也可以用HEAD~, 但是有啥有啥区别了?一个是横向的索引,看兄妹。一个是纵向的看父亲。参考stackoverflow
$ git show HEAD~~~
Commit Ranges
Double Dot
# all commits reachable from experiment that aren’t reachable from master
$ git log master..experiment
两个点
本地已经提交,但是 remote 没有的,看看领先几个commit
$ git log origin/master..HEAD
多个筛选条件,^ = – not ref ,两个点的并没有^ 好懂
$ git log refA..refB
$ git log ^refA refB
$ git log refB --not refA
$ git log refA refB ^refC
$ git log refA refB --not refC
三个点
all the commits that are reachable by either of two references but not by both of them. 找到独立的commit
$ git log master...experiment
突然想到一个问题如果想要看?log tree了,这是个简单的版本,非常方便
alias gtree="git log --all --decorate --oneline --graph"
7.2 Interactive Staging Interactive Staging
把一个大的commit 分割成几个小的,这样可以方便其他人审核代码
Interactive Staging
$ git add -i
staged unstaged path
1: unchanged +0/-1 TODO
2: unchanged +1/-1 index.html
3: unchanged +5/-1 lib/simplegit.rb
*** Commands ***
1: [s]tatus 2: [u]pdate 3: [r]evert 4: [a]dd untracked
5: [p]atch 6: [d]iff 7: [q]uit 8: [h]elp
What now>
Staging Patches
可以把一个文件的部分提交到暂存区,这个功能很有意思了,也可以通过另外一个branch的方式吧,个人不太喜欢回过头来这么做。
7.3 Stashing and Cleaning
The problem is, you don’t want to do a commit of half-done work just so you can get back to this point later. The answer to this issue is the git stash command. 如果是个人可能无所谓,但是团队合作,太多无意义的commit就会有问题,不过有merge rebase,为啥要有stash?很类似于“暂停”按钮
Stashing Your Work
如果更改了几个文件
$ git status
Changes to be committed:
(use "git reset HEAD <file>..." to unstage)
modified: index.html
Changes not staged for commit:
(use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git checkout -- <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
modified: lib/simplegit.rb
$ git stash
Saved working directory and index state \
"WIP on master: 049d078 added the index file"
HEAD is now at 049d078 added the index file
(To restore them type "git stash apply")
# 这个时候就没有暂存区的变更了
$ git status
$ git stash list
stash@{0}: WIP on master: 049d078 added the index file
stash@{1}: WIP on master: c264051 Revert "added file_size"
stash@{2}: WIP on master: 21d80a5 added number to log
$ git stash apply stash@{2}
Creating a Branch from a Stash
# 直接从stash 创建 branch
$ git stash branch testchanges
M index.html
M lib/simplegit.rb
Switched to a new branch 'testchanges'
On branch testchanges
Changes to be committed:
(use "git reset HEAD <file>..." to unstage)
Cleaning your Working Directory
# To remove all the untracked files in your working directory, you can run git clean -f
$ git clean -f
# dry run, 告诉结果,但是不会开始行动
$ git clean -d -n
7.5 Searching
也是协作的需求,找到特定的函数或者文件,这样可以追溯历史 «««< HEAD =======
Git Grep
$ git grep -n gmtime_r
$ git grep --count gmtime_r
$ git grep -p gmtime_r *.c
# --break and --heading options which help split up the output into a more readable format
$ git grep --break --heading \
-n -e '#define' --and \( -e LINK -e BUF_MAX \) v1.8.0
Git Log Searching
都是帮助追溯历史
$ git log -S ZLIB_BUF_MAX --oneline
e01503b zlib: allow feeding more than 4GB in one go
ef49a7a zlib: zlib can only process 4GB at a time
Line Log Search
这个功能感觉就是找到底谁引入的bug了, to see every change made to the function git_deflate_bound in the zlib.c
$ git log -L :git_deflate_bound:zlib.c
commit ef49a7a0126d64359c974b4b3b71d7ad42ee3bca
Author: Junio C Hamano <gitster@pobox.com>
Date: Fri Jun 10 11:52:15 2011 -0700
zlib: zlib can only process 4GB at a time
diff --git a/zlib.c b/zlib.c
--- a/zlib.c
+++ b/zlib.c
@@ -85,5 +130,5 @@
-unsigned long git_deflate_bound(z_streamp strm, unsigned long size)
+unsigned long git_deflate_bound(git_zstream *strm, unsigned long size)
{
- return deflateBound(strm, size);
+ return deflateBound(&strm->z, size);
}
7.6 Rewriting History
Git Grep
$ git grep -n gmtime_r
$ git grep --count gmtime_r
$ git grep -p gmtime_r *.c
# --break and --heading options which help split up the output into a more readable format
$ git grep --break --heading \
-n -e '#define' --and \( -e LINK -e BUF_MAX \) v1.8.0
Git Log Searching
都是帮助追溯历史
$ git log -S ZLIB_BUF_MAX --oneline
e01503b zlib: allow feeding more than 4GB in one go
ef49a7a zlib: zlib can only process 4GB at a time
Line Log Search
这个功能感觉就是找到底谁引入的bug了, to see every change made to the function git_deflate_bound in the zlib.c
$ git log -L :git_deflate_bound:zlib.c
commit ef49a7a0126d64359c974b4b3b71d7ad42ee3bca
Author: Junio C Hamano <gitster@pobox.com>
Date: Fri Jun 10 11:52:15 2011 -0700
zlib: zlib can only process 4GB at a time
diff --git a/zlib.c b/zlib.c
--- a/zlib.c
+++ b/zlib.c
@@ -85,5 +130,5 @@
-unsigned long git_deflate_bound(z_streamp strm, unsigned long size)
+unsigned long git_deflate_bound(git_zstream *strm, unsigned long size)
{
- return deflateBound(strm, size);
+ return deflateBound(&strm->z, size);
}
7.6 Rewriting History
让commit 的历史变成你想要的那样,拆分合并修改,从每一个commit 删除一个文件,修改email 地址
Changing the Last Commit
- modify your last commit message, 不管是commit 的内容还是commit message。如果要更更改内容,就直接更改在运行如下命令即可
- don’t amend your last commit if you’ve already pushed it!
- An amended commit may (or may not) need an amended commit message. 如果只是更改一下拼写错误之类的
$ git commit --amend
7.7 Reset Demystified
| Tree | Role |
|---|---|
| HEAD | Last commit snapshot, next parent |
| Index | Proposed next commit snapshot |
| Working Directory | Sandbox |
Head
通过git log 也能看到HEAD 指向情况
$ git cat-file -p HEAD
# inspecting the state of the Staging Index tree.
$ git ls-tree -r HEAD
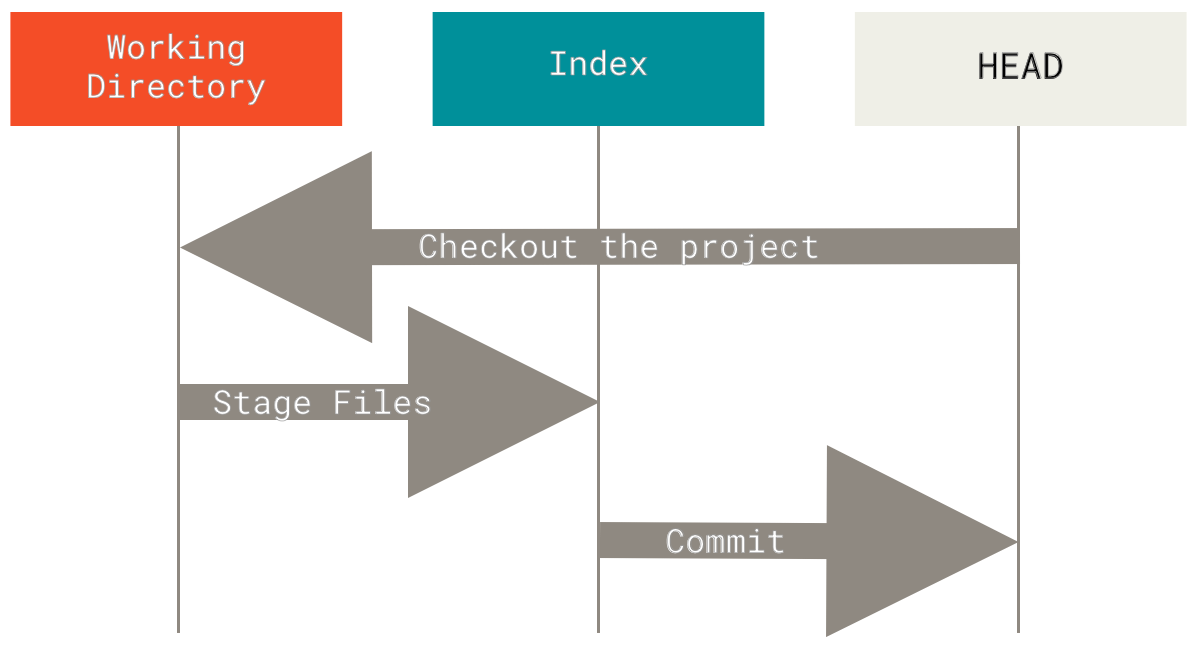
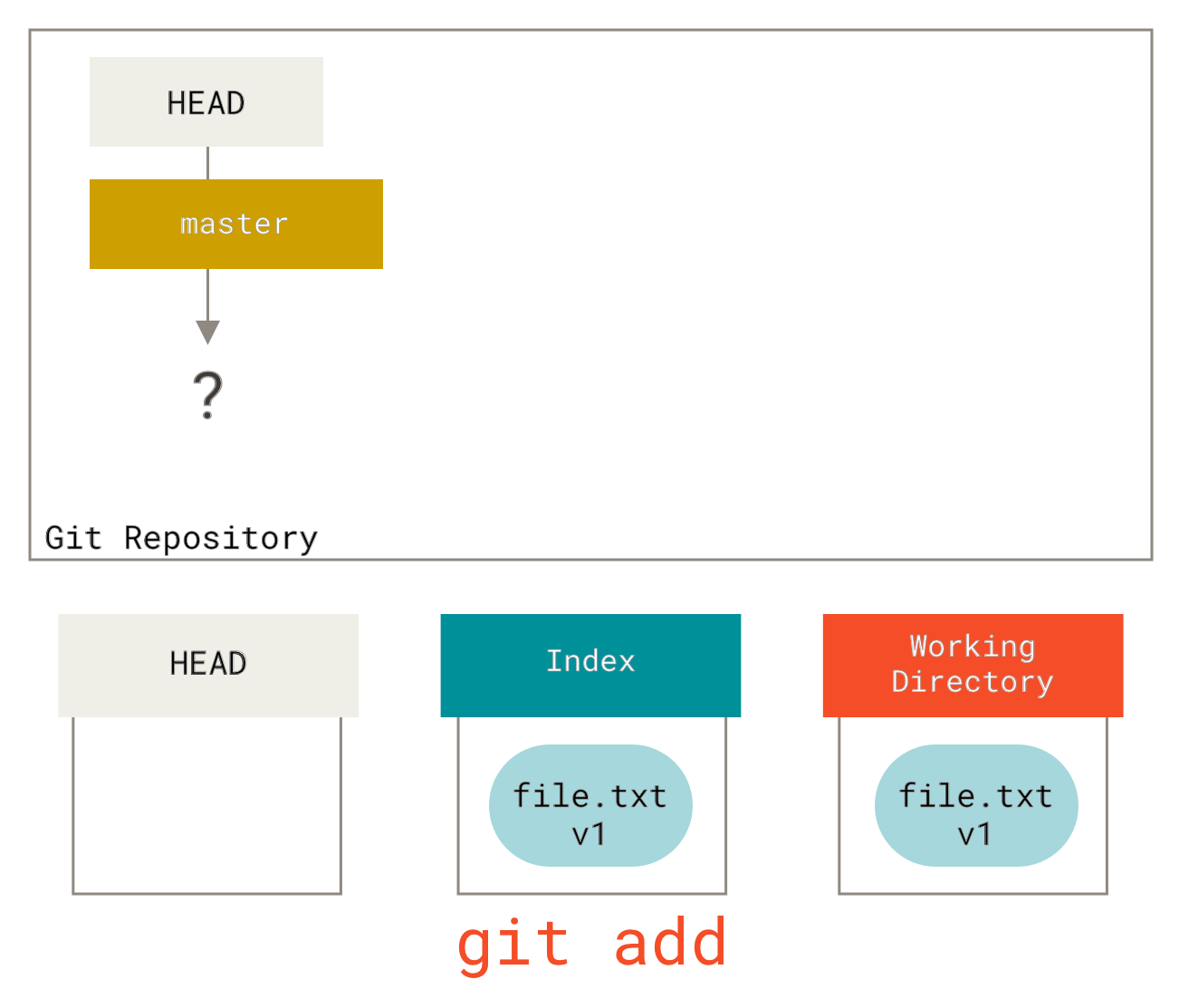
- git add 可以把file.txt 添加到index
- The git status command output displays changes between the Commit History and the Staging Index。如果红色就是working directory出现了变动,如果 git add 那么变动到了Index,git status 显示黄色